How to Fix Access is Denied, File May Be In Use, or Sharing Violation Errors in Windows
Access Is Denied Error
This particular error is normally caused by NTFS permissions, but it can also be caused by other issues like a corrupt user profile, encryption on the file or if the file is in use. We’ll talk about file in use errors in the next section.
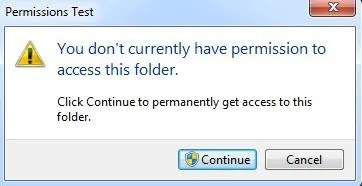
To gain access to the file or folder, you’ll need to have the correct permissions configured for your account. Before you start doing any work, you should try to click on the Continue button that will show up in Windows 7 and Windows 8 automatically. This will try to give your user account permissions to the folder as long as you are the owner.
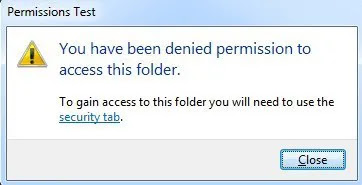
If you get the You have been denied permission to access this folder message after clicking Continue, that means you are not the owner and you’ll have to first take ownership of the folder before you can change any permissions.
Take Ownership of Files and Folders in Windows
Resolution : Grant Cmd.exe Read and Execute permissions
Linux and Unixish system comes with chmod and other commands to setup/change access permission from command line/shell.
However, when it comes to windows chmod is not available. Windows comes with a special command line utility called CACLS.
You can use it as follows:
CACLS files /e /p {USERNAME}:{PERMISSION}
Where,
- /p : Set new permission
- /e : Edit permission and kept old permission as it is i.e. edit ACL instead of replacing it.
- {USERNAME} : Name of user
- {PERMISSION} : Permission can be:
- R – Read
- W – Write
- C – Change (write)
- F – Full control
For example grant Rocky Full (F) control with following command (type at Windows command prompt):
C:> CACLS files /e /p rocky:f
Read complete help by typing following command:
C:> cacls /?
So if you want to add permissions to a folder called "Shared", located on C: drive for Everyone, do the following:
C:\cacls c:\Shared /e /p Everyone:f
Where /e is to preserve old permissions;
/p is to add new permissions;
Everyone is the user
f stands for Full Control (R Read, W Write, C Change (write), F Full control)
If you don't include /e, the permissions assigned will be the only permissions on the file/directory.

Comments
Post a Comment